Table of Contents
Objective
This lesson will show you how to make the PiBot follow a line on the ground. First it will show you how to add the Infrared (IR) sensors to the PiBot. Then it will show you how to program the PiBot to follow a line. Finally it will describe how the electronics let the PiBot “see” the line and follow it.
Parts Required
The parts below are required to complete this lesson. Note that all parts except the foam board and optional hardware are included in the OSOYOO kit that can be purchased on Amazon.
- Assembled PiBot from Lesson 1
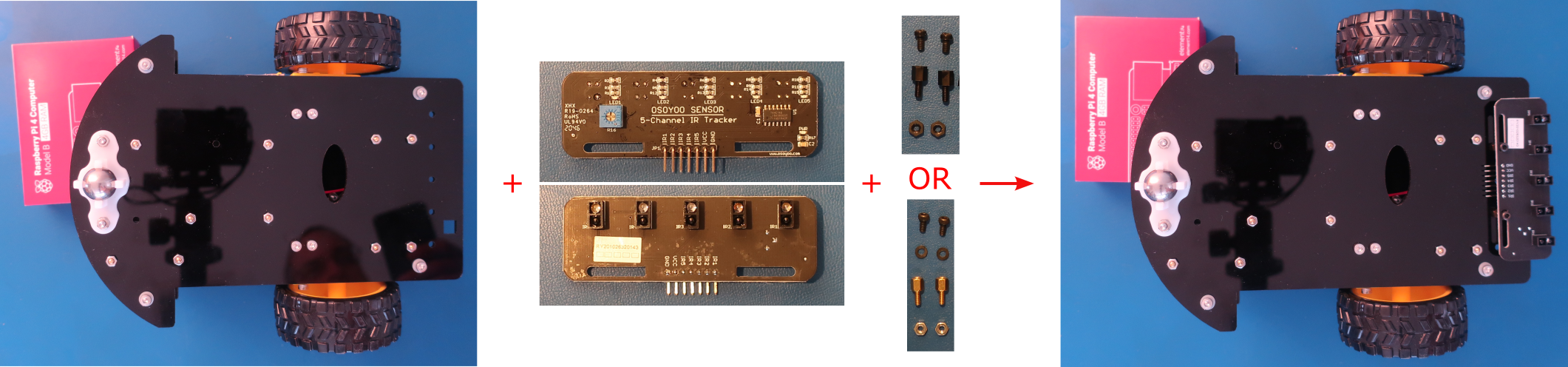
- OSOYOO Sensor 5-Channel IR Tracker Board
- 7-pin 25cm Female to Female Jumper Wires
- 3cm Wide Black Tape
- 3/16 inch thick White Foam Board or Corrugated Plastic Yard Signs
- Hardware
- M2.5x5mm Plastic Screws
- M2.5x5mm+6mm Hex Plastic Pillars
- M2.5 Hex Plastic Nuts
- Optional Hardware
- M2.5x5mm Hex Cap Screws
- M2.5x5mm+6mm Hex Brass Pillars
- M2.5 Hex Nuts
Hardware Assembly
When handling any of the circuit boards make sure to wear your ESD wrist strap and have it connected to an earth ground point
When installing items with multiple screws or nuts, leave them loose until all are installed and then tighten to ensure that you can get them all inserted
- Install the IR tracker board on the bottom chassis with 2pcs M2.5x5mm screws, M2.5x5mm+6mm pillars, and M2.5 nuts from the hardware kit as shown below
Attach the M2.5x5mm+6mm pillars to the chassis with the nuts first and then install the board with the screws
Leave the screws loose and slide the IR tracker board to align the blue potentiometer on the top with the square hole in the bottom chassis, then tighten the screws
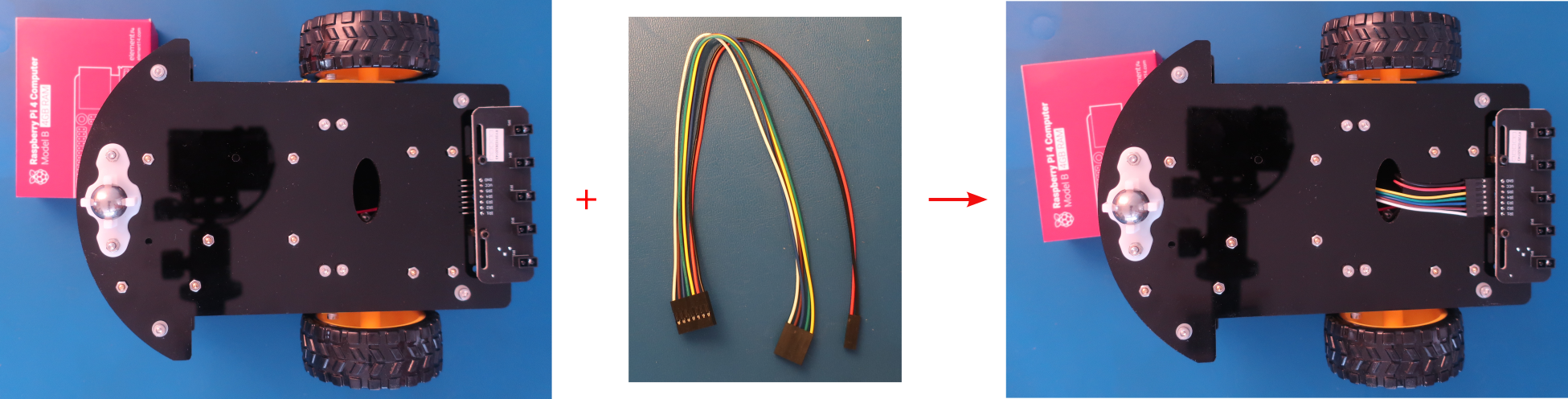
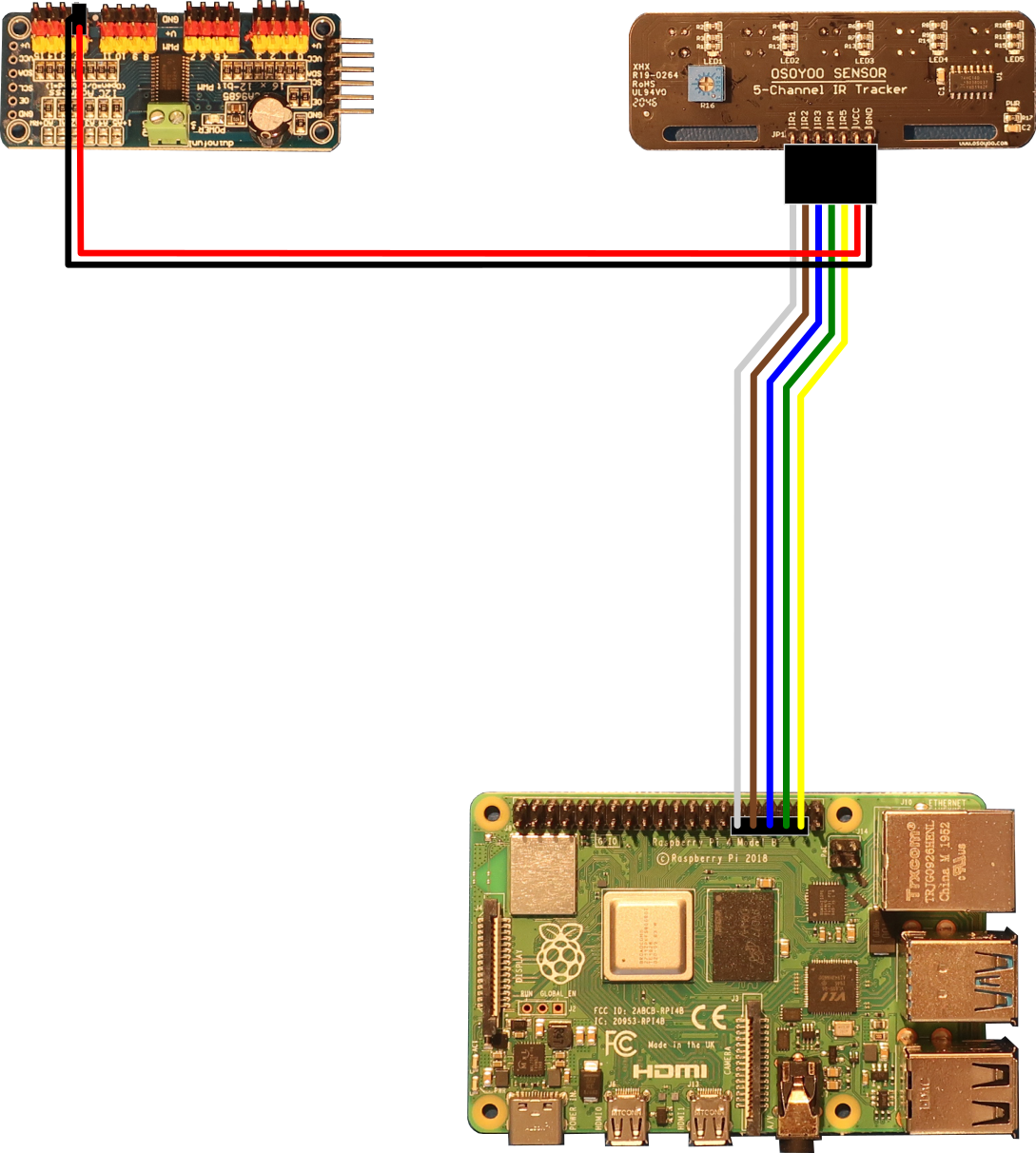
- Connect the IR tracker board to the PCA9685 compatible board and Raspberry Pi board as shown below
Create loops in the wires by wrapping them around your finger to keep the wiring neat
Feed the wires through the oval hole in the bottom chassis to get them to the PCA9685 compatible board. Feed the wires through the oval hole in the bottom chassis and the rectangle hole in the top chassis to get them to the Raspberry Pi board. Keep the wires from the IR tracker board to the oval hole in the bottom chassis straight and up against the bottom chassis so they won't drag on the ground when the PiBot moves.
IR Tracker Board PCA9685 Module Raspberry Pi Board IR1 — Pin 29 (GPIO 5) IR2 — Pin 31 (GPIO 6) IR3 — Pin 33 (GPIO 13) IR4 — Pin 35 (GPIO 19) IR5 — Pin 37 (GPIO 26) VCC V+12 — GND GND12 — - Lay out a path on the foam board with the black tape
Use small lengths of the clear packing tape to join multiple pieces of the foam board together to make a larger area for your maze. Place the tape on the top of the foam board for one joint and on the bottom of the foam board for the next joint so that you can fold it up like a Z and store it flat.
Keep any corners or bends gradual, e.g. use an 8 to 12 inch radius or larger. Use short pieces of the black tape at angles to each other to create the corners or bends.
Draw out the path that you want using a pencil and then lay the black tape over it
Software
Select the appropriate link below for instructions to setup the software on the PiBot and an exploration of how it works.
Electrical Description
The OSOYOO IR Tracker board has 5 IR sensors on on the bottom that sense the surface under the PiBot. Each sensor has a light that shines down toward the surface and a detector that senses the reflected light. The light from the sensor is Infrared (IR) which is a color that humans cannot see.
The sensor outputs a voltage that varies based on how much light is reflected back to it. When a lot of light is reflected back then the voltage is lower. Since the black tape absorbs most of the light but the white foam board reflects some of the light, the voltage from the sensor is lower for the white foam board than it is for the black tape.
The voltage from each sensor is fed into a Schmitt trigger inverter chip. When the Schmitt trigger inverter chip senses its input voltage below a threshold, it outputs a high voltage. Similarly when the Schmitt trigger inverter chip senses its input voltage above the threshold it outputs a low voltage. The threshold is usualy around half of the supply voltage of the chip. The blue potentiometer allows the voltages from the IR sensors to be adjusted so that they are above and below the threshold of the inverter chip.
The output of the Schmitt trigger inverter chip is connected to the Raspberry Pi GPIO inputs so that the software can tell when each sensor is over the black tape or the white foam board.